Orthogonality
In factorial analysis, "orthogonality" refers to variables that are independent and uncorrelated. When two factors are orthogonal, you can study their effects as if they are happening at a right angle to each other, rather than overlapping. This leads to a clearer understanding of each factor's contribution to the outcome. The opposite of orthogonal factors are oblique factors.
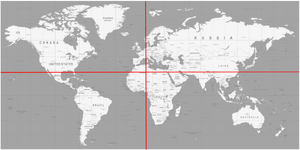
Consider the world map on the right. You may like to locate an individual on this map with its longitude and latitude. Those two dimensions are orthogonal.
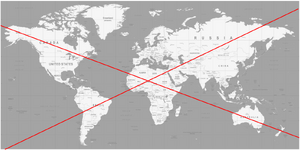
You may as well locate the individual by two oblique factors, like this other map on the right. The first one is simply more practical than the second.
So, it goes with behavioral dimensions that can be located by two, three, or four factors. Orthogonal factors allow for the location and description of behaviors when the factors are as distant from each other as possible.