GRI General Framework: Difference between revisions
m (→First Model) |
|||
| (39 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Introduction= | =Introduction= | ||
This article presents the | This article presents the general framework built at GRI to analyze the nature, use, and effect of assessment techniques on an organization's performance. Over the years, we have considered a variety of assessment techniques, including behavioral assessments and parallel techniques that we use ourselves privately, and observed the impact those techniques have on leadership, decision-making, communication, and, ultimately, on individuals and a company's performance. | ||
The | The framework was built in two phases over a 20-year period. During that period, we devised the GRI assessment and the adaptive profiles by removing the limiting factors uncovered during the first phase of the research. This has allowed us to better define what performance means at an individual and organizational level and deploy the adaptive profiles to operations and individuals in executive positions. After a brief history of the framework and its construction in two phases, this article presents and comments on its design and reviews a couple of its aspects. | ||
=First | =First Framework= | ||
The first | The first framework was built by Frederic Lucas-Conwell for his PhD thesis in the years 2002 to 2006. The thesis demonstrated the positive effects of using personality assessments by managers on individual and group performance. The assessment techniques of the early 2000s were in constant progress. Software packages were providing increasing capabilities to analyze information and compute statistics. The building of the framework followed social research academic standards, notably those of Miles and Huberman<ref>Miles M.B., Huberman A.M. (2003). Qualitative data analysis; De Boeck University.</ref>, Wacheux<ref>Wacheux, F. (1996). Méthodes Qualitatives de Recherche en Gestion. Economica.</ref>, and Eisenhardt<ref>Eisenhardt K. M. (1989). Building Theories from Case Study Research, Academy of Management Review, vol. 14, n° 4, pp. 532-550.</ref>. | ||
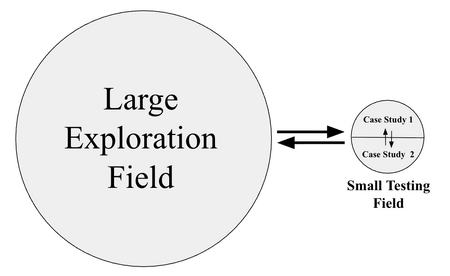
A large exploration field consisted of 1,116 people from 501 companies | A large exploration field consisted of 1,116 people from 501 companies, met from 1995 to 2006. The organizations were from varied industries, different countries, and of different sizes. It allowed the collection of information on the uses of assessment techniques, their users, and their effects. The framework was subsequently tested on two organizations, which are referred to as the case studies of the small testing field. The research process followed the diagram below. The arrows represent the interactions between the different fields. | ||
[[File:Large-Small Field.png|center|450px]] | [[File:Large-Small Field.png|center|450px]] | ||
The observations from the large field were from primary sources: direct observations of companies and their people, and secondary sources: testimony from publishing companies, consultants, journalists, and documents. The interaction between the large and small fields happened once the | The observations from the large field were from primary sources: direct observations of companies and their people, and secondary sources: testimony from publishing companies, consultants, journalists, and documents. The interaction between the large and small fields happened once the framework was built. Observations from the small field and between the two case studies stimulated new observations on the large field, and vice versa, by going back and forth between the large and small fields, but only after the testing phase started. | ||
The | The framework was successfully tested on case studies of the two small testing fields. The concepts, assessment techniques, and theories supporting the framework in psychology, sociology, social-interactionism, organizational behavior, leadership, and semiotics (the analysis and philosophy of signs) had been documented in the dissertation report. | ||
= | =New General Framework= | ||
The first | The first framework helped lay the groundwork for the second phase, which ran from 2006 to 2025. After the first framework was built, the GRI (Growth Resources Institute) was started in 2012, providing a platform for a new quality assessment. Personality research solidly confirmed the universality and nature of the factors about to be used. The Internet was available for collecting, using, and analyzing data to unprecedented levels. | ||
Although the observations were saturated after the first | Although the observations were saturated after the first framework was devised, the advent of coaching, the developments in well-being, and the use of typology assessments provided opportunities for new observations. After 2005, the large exploration fields became more centered on the US and the Bay Area. | ||
The new | The new general framework includes assessment techniques such as parallel techniques, and not only personality assessments, as in the first phase. The inclusion of new techniques allowed broader analysis and comparison of assessment techniques. As identified in the first phase, assessment techniques both compete and complement each other. The GRI survey was built by removing important limitations identified in assessment techniques during the first phase. With an increasing number of assessment techniques that can be built quickly with AI, it has become urgent to demonstrate how those assessment techniques differ, how the differences reflect in their use, and what different impacts users could expect from them. The new framework was built to answer those questions. | ||
=Framework Representation= | |||
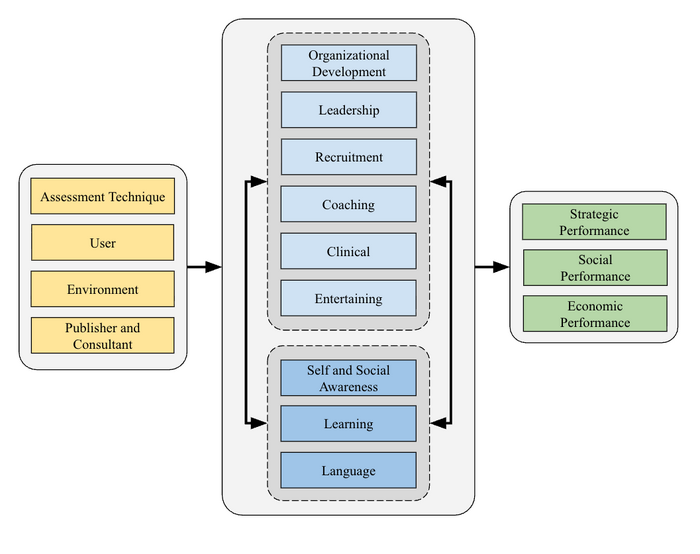
The general framework is represented below. It includes variables on the use of assessment techniques (the independent variable) and the individual, publishers, and the environment in which the techniques are used (the antecedent variable). | |||
The framework dependent variable, the organization’s performance, is contingent upon individual performance. The adaptive profiles measure and represent performance at those two levels, and subsequently assess the gap between the strategic intent on group performance and its realization. | |||
[[File:GRI Model_detailed.png|center|700px]] | |||
Different from the first framework, the number of use categories is now nine rather than six. “Clinical” was added, reflecting the increasing use of assessments by clinicians in the workplace. “Coaching” became a new category by itself. With early techniques and techniques used during large events, the framework needed a category to regroup their use, which was named “Entertaining.” | |||
The | Although the first framework discussed the parallel techniques, it didn’t include them. The new framework allows comparisons of various techniques, including new advanced techniques based on statistics, and early ones. Social performance includes a “quiet diversity” index that didn’t exist before. “Environment" includes the company's general politics, which used to be a moderating variable in the first framework. It seemed more appropriate to consider it an antecedent variable. | ||
=Notes= | =Notes= | ||
[[Category:Articles]] | [[Category:Articles]] | ||
[[Category:GRI | [[Category:GRI Framework]] | ||
Latest revision as of 01:47, 25 September 2025
Introduction
This article presents the general framework built at GRI to analyze the nature, use, and effect of assessment techniques on an organization's performance. Over the years, we have considered a variety of assessment techniques, including behavioral assessments and parallel techniques that we use ourselves privately, and observed the impact those techniques have on leadership, decision-making, communication, and, ultimately, on individuals and a company's performance.
The framework was built in two phases over a 20-year period. During that period, we devised the GRI assessment and the adaptive profiles by removing the limiting factors uncovered during the first phase of the research. This has allowed us to better define what performance means at an individual and organizational level and deploy the adaptive profiles to operations and individuals in executive positions. After a brief history of the framework and its construction in two phases, this article presents and comments on its design and reviews a couple of its aspects.
First Framework
The first framework was built by Frederic Lucas-Conwell for his PhD thesis in the years 2002 to 2006. The thesis demonstrated the positive effects of using personality assessments by managers on individual and group performance. The assessment techniques of the early 2000s were in constant progress. Software packages were providing increasing capabilities to analyze information and compute statistics. The building of the framework followed social research academic standards, notably those of Miles and Huberman[1], Wacheux[2], and Eisenhardt[3].
A large exploration field consisted of 1,116 people from 501 companies, met from 1995 to 2006. The organizations were from varied industries, different countries, and of different sizes. It allowed the collection of information on the uses of assessment techniques, their users, and their effects. The framework was subsequently tested on two organizations, which are referred to as the case studies of the small testing field. The research process followed the diagram below. The arrows represent the interactions between the different fields.
The observations from the large field were from primary sources: direct observations of companies and their people, and secondary sources: testimony from publishing companies, consultants, journalists, and documents. The interaction between the large and small fields happened once the framework was built. Observations from the small field and between the two case studies stimulated new observations on the large field, and vice versa, by going back and forth between the large and small fields, but only after the testing phase started. The framework was successfully tested on case studies of the two small testing fields. The concepts, assessment techniques, and theories supporting the framework in psychology, sociology, social-interactionism, organizational behavior, leadership, and semiotics (the analysis and philosophy of signs) had been documented in the dissertation report.
New General Framework
The first framework helped lay the groundwork for the second phase, which ran from 2006 to 2025. After the first framework was built, the GRI (Growth Resources Institute) was started in 2012, providing a platform for a new quality assessment. Personality research solidly confirmed the universality and nature of the factors about to be used. The Internet was available for collecting, using, and analyzing data to unprecedented levels.
Although the observations were saturated after the first framework was devised, the advent of coaching, the developments in well-being, and the use of typology assessments provided opportunities for new observations. After 2005, the large exploration fields became more centered on the US and the Bay Area.
The new general framework includes assessment techniques such as parallel techniques, and not only personality assessments, as in the first phase. The inclusion of new techniques allowed broader analysis and comparison of assessment techniques. As identified in the first phase, assessment techniques both compete and complement each other. The GRI survey was built by removing important limitations identified in assessment techniques during the first phase. With an increasing number of assessment techniques that can be built quickly with AI, it has become urgent to demonstrate how those assessment techniques differ, how the differences reflect in their use, and what different impacts users could expect from them. The new framework was built to answer those questions.
Framework Representation
The general framework is represented below. It includes variables on the use of assessment techniques (the independent variable) and the individual, publishers, and the environment in which the techniques are used (the antecedent variable).
The framework dependent variable, the organization’s performance, is contingent upon individual performance. The adaptive profiles measure and represent performance at those two levels, and subsequently assess the gap between the strategic intent on group performance and its realization.
Different from the first framework, the number of use categories is now nine rather than six. “Clinical” was added, reflecting the increasing use of assessments by clinicians in the workplace. “Coaching” became a new category by itself. With early techniques and techniques used during large events, the framework needed a category to regroup their use, which was named “Entertaining.”
Although the first framework discussed the parallel techniques, it didn’t include them. The new framework allows comparisons of various techniques, including new advanced techniques based on statistics, and early ones. Social performance includes a “quiet diversity” index that didn’t exist before. “Environment" includes the company's general politics, which used to be a moderating variable in the first framework. It seemed more appropriate to consider it an antecedent variable.